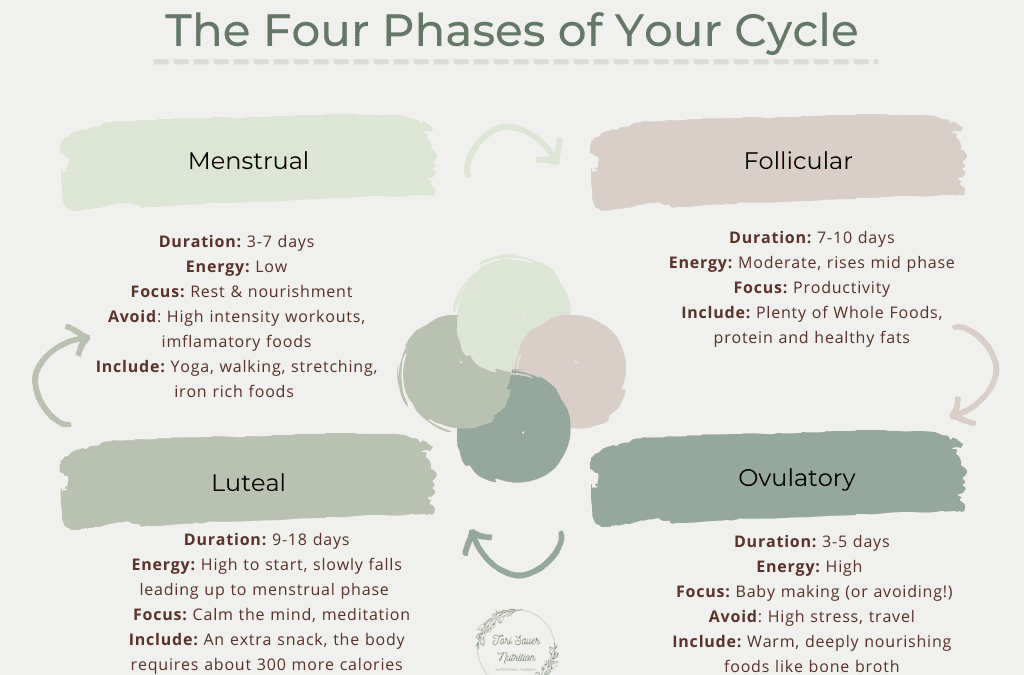
The menstrual cycle is a complex but vital process that every woman experiences. It consists of four main phases, each with its own hormonal changes and unique characteristics. Understanding these phases can help you better manage your health and well-being throughout the month.
Menstrual Phase
Duration: Average 3-7 days
Hormonal Status: Hormone levels are at their lowest
Physical Experience: Shedding of uterine lining, fatigue, low energy
Self-care Tip: It’s okay to rest and relax during this time. Including anti-inflammatory foods in your diet during this time can help to ease symptoms.
Follicular Phase
Duration: Average 7-10 days
Hormonal Status: Estrogen and testosterone levels rise
Physical Experience: Energy levels start to increase, mood improves mid-phase
Key Event: Follicular stimulating hormone released from the pituitary gland signals follicles in the ovaries to mature.
Ovulatory Phase
Duration: Average 3-4 days
Hormonal Status: Estrogen and testosterone peak
Physical Experience: High energy, confidence, increased libido
Key Event: Release of one egg from the follicle, ready for fertilization.
Luteal Phase
Duration: Ideally 9-18 days. The length of the luteal phase is crucial so that the fertilized egg has enough time to implant.
Hormonal Status: Progesterone levels will rise if fertilization has occurred. If no fertilization has occurred, progesterone levels will drop, signaling your menstrual phase.
Physical Experience: Caloric needs increase (about 300 extra calories/day)
Key Event: Preparation of the uterus for potential implantation of a fertilized egg.
Tracking Ovulation
Accurately tracking ovulation can help you understand your fertility and menstrual health better. Here are several methods you can use:
- Calendar Method: Track your cycle length to estimate ovulation.
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT): Measure your BBT upon waking to detect a slight rise indicating ovulation has occurred.
- Cervical Mucus Checks: Observe changes in cervical mucus texture (clear, stretchy, slippery) indicating fertile days.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Strips: Test urine for LH surge, indicating ovulation will occur soon.
- Progesterone Testing: Assess progesterone levels to confirm ovulation and hormonal balance.
- Body Check: Monitor emotional stability and physical symptoms (motivation, mucus, energy, libido, temperature changes) throughout the cycle.
Signs of a Healthy Period
A healthy menstrual cycle often exhibits these characteristics:
- Regular timing (arrives about the same time each month)
- Minimal to no PMS symptoms
- Bleeding lasts 3-7 days
- Total blood loss of 30-60 ml
- Bright cranberry red color (may darken towards the end)
- Smooth consistency with few to no clots
- Minimal discomfort and pain